Excel Cheat Sheet Basic Skills The Excel Program Screen Keyboard Shortcuts Getting Started Create a Workbook: Click the File tab and select New or press Ctrl + N. Double-click a workbook. Open a Workbook: Click the File tab and select Open or press Ctrl + O. Select a recent file or navigate to the location where the file is saved. Nov 03, 2005 When planning Excel 12, we started a small investigation to look at different ways we could make Excel calculate faster on computers that had multi-processor or dual-core chips. The investigation turned out to be promising, so we continued the work, and the result is a very exciting feature that we refer to as multi-threaded calculation, or MTC. Excel grouping tips. As you have just seen, it's pretty easy to group rows in Excel. Below you will find a few useful tricks that will make your work with groups even easier. How to calculate group subtotals automatically. In all of the above examples, we have inserted our own subtotal rows with SUM formulas.
- Excel Manual Calculation Key Macminerenew Programming
- Excel Manual Calculation Mode
- Excel Manual Calculation Key Macminerenew Problems
- Excel Manual Calculation Mode
- Excel Manual Calculation
Iterative calculations can help find the solution to mathematical problems by running calculations over and over using previous results. This is made possible by computers that can run calculations repeatedly to find the likelihood of possible answers by getting closer to the results from different angles.
In Excel, you can reference a cell that contains a formula and use its result in an identical formula in a different cell. For this, you would need to copy the formula and references as many times as you want to repeat the process. This can work if your model is relatively simple, but doing so in more complicated workbooks might prove much more challenging, if not downright impossible to do.
An alternative and better approach is to use the Excel iterative calculation feature. You can create a formula that refers to the cell containing the formula. The formula can use the result of the previous calculations, thus automatically calculating the same thing over multiple iterations.
As easy as it sounds, there are a few things you need to consider. First of all, the number of iterations should be limited. Even though a higher iteration count usually means more accurate results, this also means longer calculations times – and sometimes crashes. Another thing to note is that when iterative calculations are disabled, Excel will show a warning as circular references are usually considered user errors unless you know what you’re doing.
To learn more about circular references please see: How to Handle Circular References in Excel
To activate and use circular references, you must first activate them by checking Enable iterative calculations option under the File menu.
Go to File > Options > Formulas > Calculation options section in Excel 2016, Excel 2013and Excel 2010.
In Excel 2007, go to Office button > Excel options > Formulas > Iteration area.
In Excel 2003 and earlier, go to Menu > Tools > Options > Calculation.
Enabling iterative calculations will bring up two additional inputs in the same menu:
- Maximum Iterations determines how many times Excel is to recalculate the workbook,
- Maximum Change determines the maximum difference between values of iterative formulas. Note that entering a smaller number here means more accurate results.
Iterative calculations stop when one of the conditions defined (iterations count or change value) are matched. For example, let’s assume that Maximum Iterations is set to 100 and Maximum Change to 0.001. This means that Excel will stop calculating either after 100 calculations, or when there’s less than 0.001 difference between the results.
Excel Manual Calculation Key Macminerenew Programming
Calculating Future Value of an Investment
Let’s assume that we have $10,000 and want to invest this money in a cash deposit (CD) account. We’re going to assume a monthly interest rate of 1.25%. You can download the sample workbook for this use case . To calculate the total value at the end of the 21st month, we’re going to calculate the principal for each month, and add the interest to the previous month.
Begin by entering the starting cash, interest, and the total value function like below.

=value * ( 1 + interest rate)

Then, select the cell with the initial cash value and add the reference of the total value function.
This will give a circular reference warning if iterative calculations are not enabled. If you haven’t done so already, enable this option and set the Maximum Iterations to 20 to find the interest for the 21st month. See the previous section Enabling Iterative Calculations to enable this feature.
Automatic Timestamp
Circular references can also be used to add time stamps into cells. You can download the sample workbook for this use case . Let’s assume we want to add time stamps to the orders entered in the table below.
We can use circular references to add a time stamp when a new order information is entered. To do this, begin by adding a new column into the table where you’d like to print the timestamps. Type in the formula,
=IF(A2<>””,IF(I2<>””,I2,NOW()),””)
Excel Manual Calculation Mode
This formula will check whether there’s data in Order Number (cell A2). If it’s not blank and the timestamp cell is empty, the formula will return the NOW() function.
Note that pressing the Enter key will give a circular reference warning if iterative calculations are not enabled. See the previous section Enabling Iterative Calculations to enable this feature. This time Maximum Iterations or Maximum Change numbers don’t mean much, because we only need a single iteration, so you can leave these two inputs in their default values.
Now, every time we enter a new order and create a new row, a timestamp will be automatically printed on the Timestamp column.
Are you someone who has been struggling with trying to manually calculate only the active worksheet in Excel? Do you have big Excel workbooks with a lot of worksheets containing calculations and formulas? When a recalculate is performed, by default, Excel calculates all open workbooks automatically when changes are made to the worksheet. Thus, you will end up wasting a lot of time on recalculations.
Excel Manual Calculation Key Macminerenew Problems
Worksheet and Workbook Recalculation: What You Need to Know
But don’t worry, you can overcome this problem with some simple tweaks. You must select to recalculate only the active worksheet manually. It is very important to remember that you can only calculate the active worksheet within a workbook manually in Excel. There is no direct way to manually calculate only the active workbook in Excel.
Excel Manual Calculation Mode
Steps to Manually Calculate Only the Active Worksheet
Step 1: Open the Excel workbook.
Step 2: Click on the File tab or the Office button on the top extreme leftmost corner.
Step 3: Click on the ’Excel Options’ button in the backstage screen.
Step 4: In the Excel options dialog box, click on the second tab called “Formulas” from the list of options displayed on the left side.
Step 5: Under Worksheet Options in the section named Calculation Options, , click on the radio button “Manual.” By doing this, you will be able to manually calculate only the active worksheet for each and every worksheet.
Step 6: Click on the OK button.
Recalculate Workbook Before Saving Check Box
As soon as you select the Manual radio button in Step 5, the “Recalculate workbook before saving” check box gets ticked automatically. If you have the habit of saving your worksheet frequently, then you can click on the option checkbox so that it is not checked (i.e. the tick is removed/turned off). This is done to avoid wasting time on recalculation every time you simply want to save your work.
Automatic Except for Data Tables Option
Whenever a worksheet is recalculated, data tables will also be recalculated. Now, consider that you have plenty of data tables in your worksheet and you haven’t changed anything in all of the data tables. Even using the option to manually calculate only the active worksheet, while recalculating your workbook it is better to choose the “automatic except for data tables” option. When this option is selected, the data tables will be left out of the recalculation and everything else will be recalculated. This will save a lot of time on recalculating when you manually calculate only the active worksheet.
Quick Way of Turning on Manual Recalculation of Worksheets
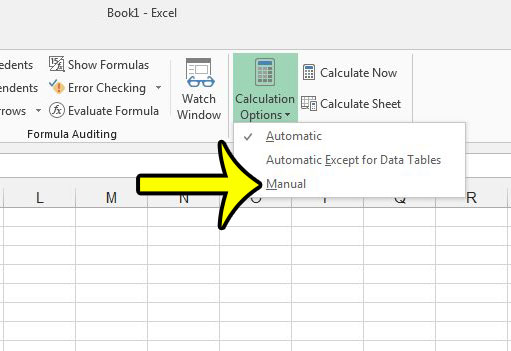
Excel Manual Calculation
Keeping the “Recalculate Workbook before saving” check box enabled, you can choose to manually calculate only the worksheets quickly. For this, click on the Formulas tab. Now click the “Calculation Options” and choose “Manual” from the drop down menu. Now, go to the Calculation section of the Formulas tab and click on Calculate Sheet. Alternatively, use the keyboard shortcut Shift+F9. This will recalculate the active worksheet manually.
By following the steps given above, you can manually calculate only the active worksheet in Excel.
